Leave Your Message
The USART/UART Serial Port LCD Module plays a crucial role in communication between devices. This technology is widely used in embedded systems. It allows for serial data transmission, offering a simple way to interface with various components.
At its core, the USART/UART module converts parallel data into a serial format. This conversion is essential for effective communication. It connects microcontrollers with LCD displays, facilitating smooth data exchange. Thus, engineers often rely on this module in their projects.
However, working with USART/UART can pose challenges. Debugging issues like baud rate mismatches or connection failures is common. Understanding the module’s capabilities and limitations is essential for troubleshooting. By mastering its functionality, users can create more reliable and efficient systems.
USART (Universal Synchronous/Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) and UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) are fundamental components in serial communication. They allow devices to send and receive data. These protocols are crucial in embedded systems, telecommunications, and industrial applications. According to a recent industry report, the global serial communication market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.2% from 2021 to 2026.
UART operates in an asynchronous manner, meaning it does not need a separate clock signal. This makes it simple and cost-effective for many applications. In contrast, USART supports both synchronous and asynchronous modes, providing flexibility for different scenarios. The key advantage of USART is its ability to synchronize data transmission, which reduces errors. However, this added complexity can lead to challenges in implementation. Many engineers struggle to balance performance and simplicity.
**Tip:** When working with UART and USART, always consider your project's specific needs. Sometimes, the simplest solution can yield the best results. If your application requires high-speed data transfer, USART may be the better choice. Always keep the communication distance in mind as well; longer distances may necessitate more robust protocols.

Serial ports play a crucial role in communication technology. They are vital for transmitting data between microcontrollers and other devices. The most common implementations include USART and UART. These protocols allow devices to connect and exchange information seamlessly. According to a recent industry report, over 40% of embedded systems depend on serial communication for effective operation.
When we connect an LCD module through a serial port, a series of signals cause the display to show the output. Sending data involves a simple process. The microcontroller sends bits one at a time. Each bit is transmitted in succession. This method reduces the complexity of wiring, making it efficient. However, the challenge lies in ensuring data integrity. Interference and noise can corrupt signals, leading to errors.
Despite their advancements, serial ports have limitations. Speed is one common issue. Many systems can struggle to maintain high data rates over longer distances. The theoretical throughput of standard serial ports is only 115.2 kbps. Real-world applications often show decreased performance. Maintaining accurate communication remains a concern, highlighting the need for constant improvements.
The LCD module is a vital component in many electronic projects. It allows users to display information in a clear and user-friendly way. These modules typically use a series of liquid crystals to create text and images. The backlight is often white or blue, making it easy to read in various lighting conditions.
Functions of the LCD module include displaying text and graphics. Developers often rely on LCDs to present real-time data. With various sizes available, hobbyists can choose the best fit for their projects. It’s common to see these modules in robotics, medical devices, and home automation systems. However, integrating an LCD can be tricky. Incorrect wiring may lead to dim displays or no output at all.
Uses of LCD modules extend beyond simple displays. They can serve as menus or settings interfaces. Sometimes, the display can freeze, causing frustration. It’s crucial to debug interactions between the microcontroller and the module. This hands-on experience offers valuable learning opportunities, revealing the nuances of electrical design and programming.
USART and UART are critical components in the realm of electronics, especially when combined with LCD modules. They serve as communication protocols, enabling devices to transmit and receive data efficiently. In many electronic projects, these protocols are imperative for achieving seamless interaction between microcontrollers and peripherals like LCD displays.
When data is sent from a microcontroller using UART, it converts the information into serial format. This step is essential for communicating with the LCD module. The LCD then interprets this serial data, showing it as text or graphics on its screen. It’s a straightforward process, but many beginners overlook the importance of proper baud rate settings. Mismatched settings can lead to garbled output, causing frustration during development.
Combining UART with an LCD module allows for dynamic content updates. Developers can send real-time data, like sensor readings, directly to the display. However, delays in communication can occur, disrupting the user experience. Ensuring a smooth flow requires careful programming and sometimes even further optimization. It's a learning curve, as every project presents unique challenges that can prompt reflection on communication techniques. The interplay between USART, UART, and LCD is both powerful and intricate. Understanding these connections is vital for successful electronic designs.
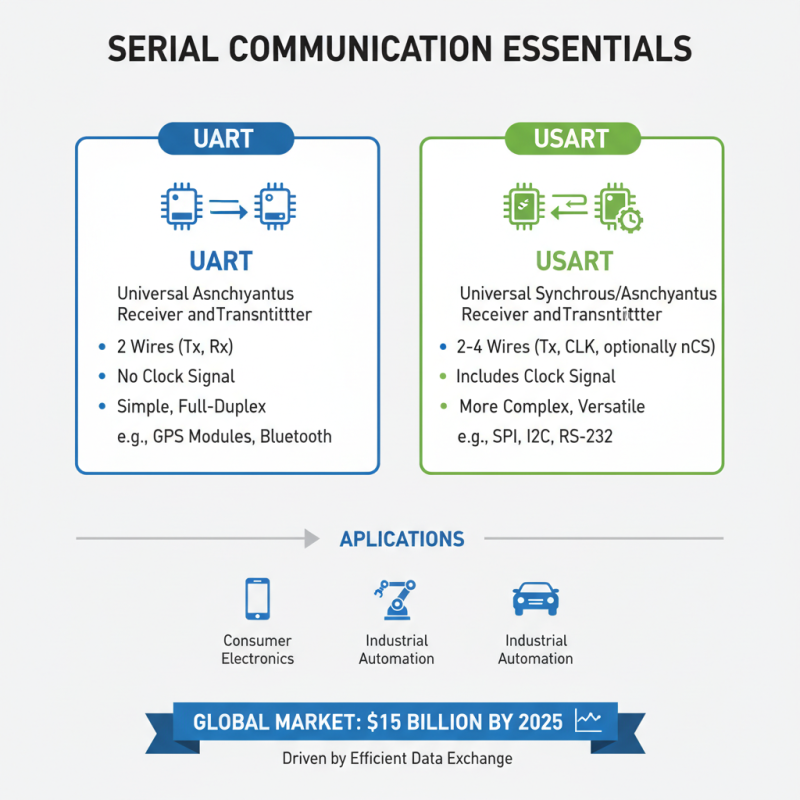
USART and UART are crucial in serial communication. They enable data transfers between microcontrollers and various peripherals. Applications range widely, from consumer electronics to industrial devices. According to a recent market research report, the global serial communication market is expected to reach $15 billion by 2025, driven by the growing demand for efficient data exchange.
LCD modules play an essential role in user interfaces. They display real-time information, making it easier for users to interact with devices. Common uses include smart appliances, medical devices, and automotive displays. A high percentage of electronic projects utilize these LCD modules. Issues arise sometimes, such as compatibility or display quality. Trouble shooting these can be complex. Ensuring robust connections and power supply can help minimize such problems.
While the benefits are clear, challenges remain. Mechanical failures and coding errors occur frequently. The intricacies of configuring USART settings may confuse beginners. Continued learning and practice can overcome these hurdles. Each application offers lessons learned, shaping future designs and implementations.