Leave Your Message
Choosing the right Embedded LCD Display can make or break your project. As John Smith, an industry expert, states, "A well-chosen display enhances user experience." This insight highlights the significance of careful selection in improving functionality.
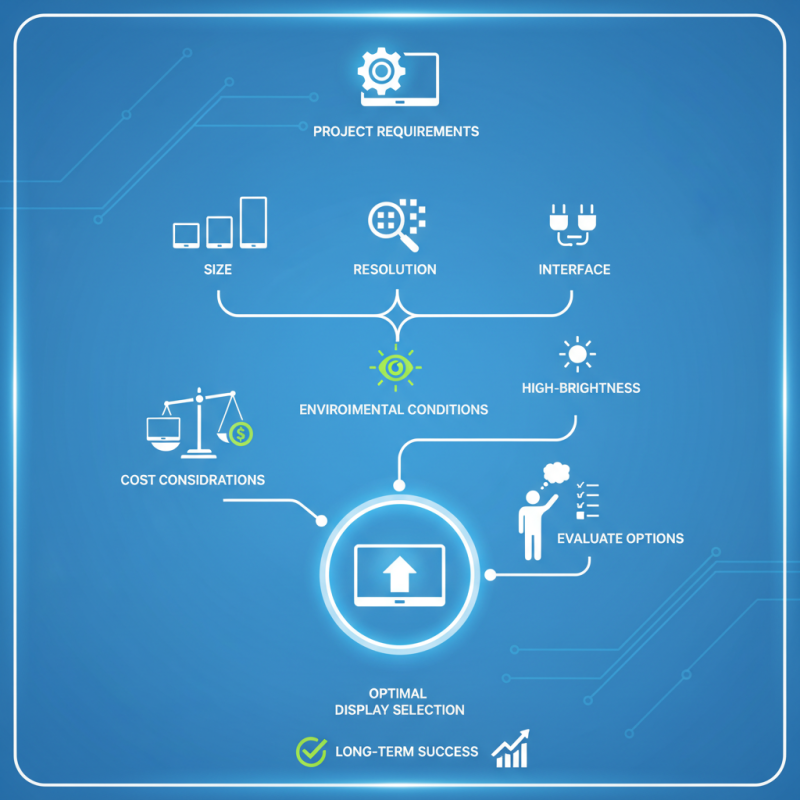
Embedded LCD Displays must match project requirements. Factors like size, resolution, and interface matter. A display that’s too small may hinder visibility. Conversely, a large one can increase costs significantly. It’s crucial to find that perfect balance. Too often, developers overlook these details, leading to issues later on.
Many fail to account for environmental conditions. Will the display face bright sunlight? If so, consider high-brightness variants. Remember, not all Embedded LCD Displays are made equal. This choice is critical for long-term success. Evaluate your options wisely to avoid costly mistakes down the road.
When selecting an embedded LCD display for your project, it's crucial to understand the different types available. The most common types are TFT, OLED, and character displays. Each has unique characteristics that suit different applications.
TFT displays offer vibrant colors and good resolution. They are ideal for applications requiring detailed images.
OLED displays deliver excellent contrast and deep blacks. They are perfect for portable devices due to their low power consumption.
Meanwhile, character displays are simple and cost-effective, suitable for displaying text and basic graphics.
Tip: Consider the environment where your display will be used. For outdoor use, opt for displays with higher brightness.
It's important to reflect on your project needs. Are you focusing on cost, size, or power usage? Often, the best choice may not be the most expensive option. For example, a simple character display might meet your needs without the added complexity of a TFT.
Tip: Evaluate your display's resolution against your design. A high resolution isn't always necessary. Sometimes, simpler displays suffice, saving both complexity and cost.
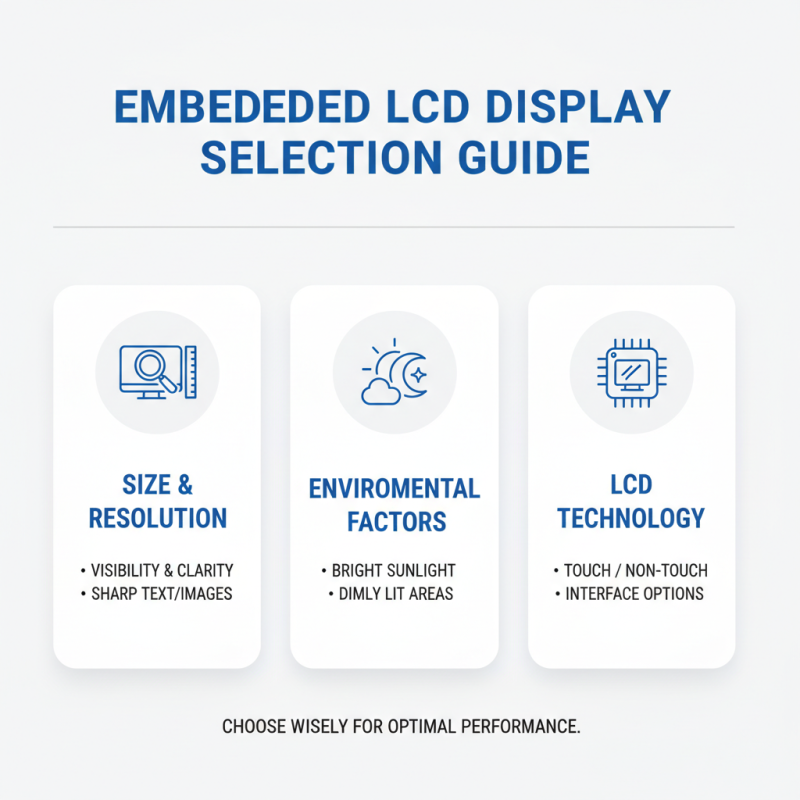
When selecting an embedded LCD display, several key factors should guide your decision. Consider the size and resolution of the display. The size affects visibility, while resolution impacts clarity. A high-resolution screen can make text and images sharper. Think about the environment too. Will the display be in bright sunlight or a dimly lit area? This influences your choice.
Tips: Choose an LCD with good brightness levels and contrast ratios for challenging environments. Testing a few options before finalizing is a wise move.
Next, think about the interface. Different projects require various communication protocols. Make sure the display is compatible with your microcontroller or processor. This is critical for functionality. Don’t overlook power consumption either. A display that consumes too much power may not be suitable for battery-operated devices.
Tips: Evaluate the power requirements. Always consider future upgrades when selecting a display. This helps avoid constraints later in the project development. Remember that integrating a display isn’t just plug-and-play. It can be a process filled with adjustments. Be prepared to rethink your choices as your project evolves.
Choosing the right embedded LCD display is crucial for project success. Evaluating key factors like size and resolution directly impacts performance and user experience.
For instance, a display’s resolution affects image clarity. Higher resolutions like Full HD (1920x1080) often offer better visual quality. However, they can consume more power and may lead to overheating issues.
The display size should align with the intended use. A common thumb rule is to select sizes between 5 to 10 inches for portable devices. As per industry reports, displays below 7 inches are usually more energy efficient. Yet, they might not provide sufficient screen space for complex data presentations. Conversely, larger displays can enhance visibility but increase device bulk and power draw.
Balancing these elements can be tricky. While larger sizes and higher resolutions seem appealing, they also demand more processing capacity. Device compatibility with these displays can pose challenges. It is vital to consider these factors during the planning process.
User feedback highlights frustrations with poor visibility and responsiveness. Therefore, thorough evaluation of size and resolution is essential for optimal performance.
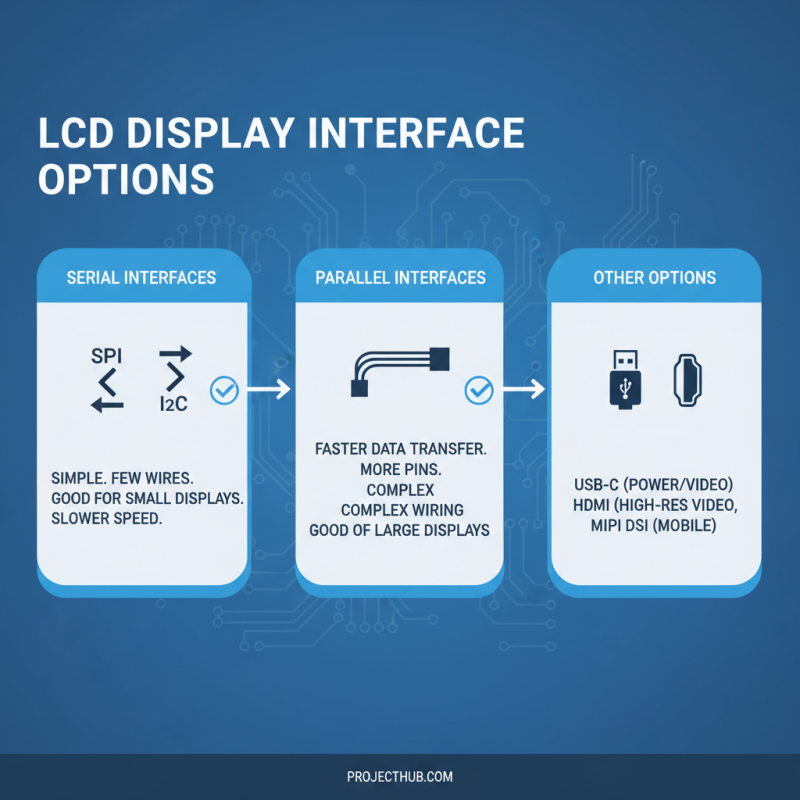
When integrating an embedded LCD display into a project, it’s crucial to consider the interface options available. Different projects demand various connections. For example, serial interfaces like SPI and I2C are popular choices due to their simplicity and effectiveness. They're easy to implement, but can be slow with larger displays.
Another option is parallel interfaces. These provide faster data transfer rates, which can enhance performance in graphics-intensive applications. However, they require more pins and can complicate design. It’s a balancing act between speed and complexity that needs careful thought.
Additionally, not all displays support every interface. Some may offer multiple interfaces, while others do not. Double-checking the specifications is a must. Understanding your project’s specific needs is essential. Take note; sometimes, the best choice is not the fastest or simplest but the one that best meets your goals. This requires critical thinking and reflection on potential challenges, shaping your final decision.
When selecting an embedded LCD display, attention to power consumption is crucial. Low power displays can enhance battery life, reducing costs in projects. Often, energy-efficient displays use advanced technology to minimize consumption. Check specifications carefully. Aim for a balance between visibility and energy needs. High brightness may draw more power, leading to trade-offs.
Environmental requirements also play a significant role. Consider the operating temperature range. Extreme conditions can affect display performance. For example, displays in outdoor equipment need better sunlight visibility and durability. Moisture resistance is another factor. Displays used in humid environments should withstand condensation to avoid damage.
Reflect on your specific use case. Think about how the display will be used daily. Is it stationary or mobile? How often will it be turned on? These questions can guide decisions. Power management features, like dimming capabilities, should not be overlooked. Test potential displays in real-world settings. Actual performance can differ from specs. Understanding these factors will help in creating a successful project.






