Leave Your Message
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, the integration of an Embedded LCD Display into various applications has become more critical than ever. As projected by industry analysts, the global embedded display market is anticipated to reach $16 billion by 2025, driven by the demand for high-quality visual interfaces in sectors such as consumer electronics, industrial automation, and automotive systems. This growth underscores the importance of selecting the right Embedded LCD Display for specific projects, as the performance and functionality of these displays can significantly impact user experience and project success.
Choosing an appropriate Embedded LCD Display requires a careful consideration of various factors, including resolution, brightness, power consumption, and interface compatibility. According to recent market research, manufacturers and developers are increasingly focusing on energy-efficient display technologies to meet consumer demand for sustainable solutions. As the IoT (Internet of Things) continues to expand, the need for displays that provide seamless connectivity and integration with smart devices is paramount.
As we delve into the intricacies of selecting the best Embedded LCD Display for your project, it is essential to align your choices with both technical specifications and market trends. By understanding the critical parameters and leveraging the latest industry insights, you can make informed decisions that not only enhance the functionality of your application but also contribute to the overall success of your project in a competitive marketplace.

When selecting an embedded LCD display for your project, it is essential to grasp the core technologies that power these displays. LCD, or Liquid Crystal Display, operates on the principle of manipulating light through liquid crystals sandwiched between layers of glass. This technology can be categorized into two primary types: passive matrix and active matrix. Passive matrix displays are simpler and more cost-effective, but they tend to offer lower resolution and slower response times. Active matrix, often referred to as Thin Film Transistor (TFT) technology, provides superior image quality and faster refresh rates, making it more suitable for applications requiring high-resolution visuals.
In addition to understanding the types of LCD technologies, it is also crucial to consider the essential specifications that impact performance. Factors such as screen size, resolution, brightness, and contrast ratio play significant roles in how the display will perform in various environments. For instance, a display with higher brightness levels may be necessary for outdoor use, while higher resolutions are vital for applications needing detailed imagery.
Furthermore, viewing angles can vary significantly between different LCD technologies, which can affect usability depending on how the display will be positioned. By mastering these fundamentals, you will be better equipped to choose the right embedded LCD display that meets your project's specific needs.
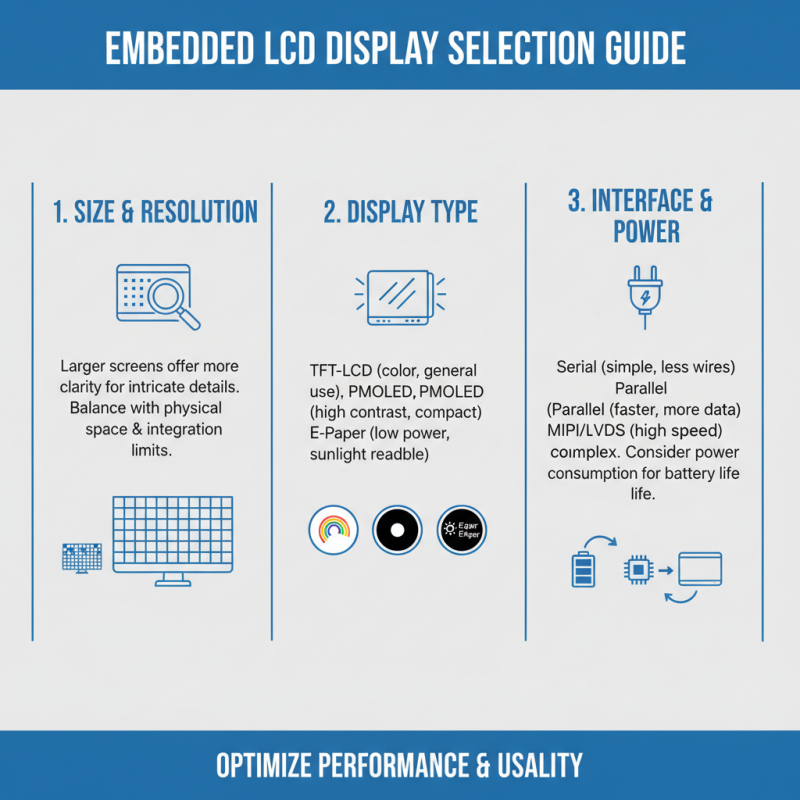
When it comes to selecting an embedded LCD display for your project, there are several key factors to consider that can significantly impact performance and usability. First, assess the display size and resolution based on your application requirements. Larger screens with higher resolutions provide better clarity and detail, which is crucial for applications that demand intricate visual feedback. However, physical space and integration constraints may dictate the maximum size you can work with, making it essential to strike a balance between screen real estate and overall design simplicity.
Another important factor is the display technology used, including considerations such as brightness, contrast ratio, and viewing angles. These attributes play a vital role in ensuring that the display remains legible under various lighting conditions and can be viewed comfortably from different angles. Additionally, consider the power consumption of the display and its compatibility with your project's energy requirements. Low-power displays may be essential for battery-operated devices, where efficiency is key to prolonging operational lifetimes. Taking these factors into account will help you choose the most suitable embedded LCD display that meets both technical specifications and user experience expectations.

When selecting an embedded LCD display for your project, evaluating size and resolution is paramount, as these factors can significantly influence both the user experience and the functionality of the device. The size of the display should be aligned with the intended application. For example, larger screens may enhance usability in systems that require detailed graphical output or interfaces, such as industrial control panels or advanced consumer devices. Conversely, compact displays are ideal for portable gadgets where space is a premium, ensuring that they are still manageable in terms of both ergonomics and integration into existing systems.
Resolution is equally crucial because it determines the clarity and quality of the images and text displayed. High resolution allows for finer details and better readability, which is essential in applications involving intricate graphics or critical information presentation. For projects that involve displaying images, animations, or high-definition content, opting for displays with higher pixel densities can greatly improve the visual output. However, it is important to strike a balance—overly high resolution may demand more processing power and can complicate integration in terms of power consumption and cost. Thus, assessing the specific requirements of your project will guide you in choosing the optimal size and resolution for your embedded LCD display.
When selecting an embedded LCD display for your project, understanding the
connectivity options and their
compatibility with your system is crucial. According to a report by
MarketsandMarkets,
the global embedded display market is expected to reach
$22 billion by 2025,
highlighting the increasing importance of these components in modern applications.
Key connectivity options include HDMI,
LVDS, and
MIPI DSI, each offering unique advantages depending
on the requirements of the project. For instance, HDMI is widely used for its
plug-and-play simplicity and high definition,
while LVDS allows for lower power consumption and higher data rates, essential for
applications needing fast video performance.
Another important aspect to consider is the
compatibility of the display
with your existing hardware and software systems. A growing trend in the industry,
as noted by
Grand View Research,
emphasizes the need for displays to integrate seamlessly with
microcontrollers and embedded systems.
Ensuring compatibility not only reduces development time but also minimizes potential
integration issues. For example, the use of standard interfaces like
I2C or
SPI can greatly enhance communication
between the display and other hardware components, leading to improved overall performance.
Thus, thorough evaluation of connectivity options and compatibility with your system
is vital to the success of your
embedded display project.
When planning to incorporate an embedded LCD display into your project, understanding cost considerations is crucial. As of late 2023, the market for embedded displays is projected to reach approximately $10 billion by 2026, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5.5%. This growth is driven by the increased demand in various sectors such as consumer electronics, automotive, and industrial applications. Therefore, it is imperative to assess both upfront and long-term costs associated with such displays to ensure that your budget aligns with your project's needs.
When determining the budget for an embedded LCD display, factors like screen size, resolution, and customization options play a significant role. A recent industry report indicates that high-resolution displays can cost 20-30% more than standard displays, while custom designs may increase overall expenses by up to 40% due to added development and manufacturing processes. Additionally, it is important to factor in potential costs related to integration and testing, which can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the interface with your existing systems. Careful budgeting and proper allocation of resources toward selecting the right display not only help in optimizing expenses but also enhance the overall functionality and user experience of your project.
| Parameter | Description | Cost Range (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Screen Size | Diagonal measurement of the display (in inches) | $20 - $500 |
| Resolution | Number of pixels in each dimension (e.g., 800x480) | $30 - $700 |
| Brightness | Measured in nits; affects visibility in different lighting | $25 - $400 |
| Interface Type | Communication protocol (e.g., SPI, I2C, HDMI) | $15 - $300 |
| Viewing Angle | Maximum angle at which the display can be viewed sans distortion | $20 - $250 |
| Power Consumption | Average power usage (in watts) | $10 - $200 |
| Temperature Range | Operating temperature limits (in Celsius) | $15 - $150 |






